| e-DBI: e-Science Database Integrator |
Project description:
e-DBI is a database application that allows the scientists to seamlessly connect to several of multi-format data sources.
It facilitates the navigation and exploration of scientific data sources with potential for data integration.
In a typical integration scenario, the scientists need to perform several activities and tasks to gather and collect
all the information from the different data sources. With e-DBI, however, these tasks are performed in a single-access point,
while the integration is carried out by defining a virtual database based on the collected data sources. Furthermore,
the e-DBI tool uses a relational backend, enabling customizations for the location and format of the virtual database.
The tool e-Science Database Integrator (e-DBI) aims at providing a data access interface more suitable to scientists.
As shown in Fig.1, a scientist needs consider the following steps to define a virtual (integrated) database:
- 1. Define a virtual database (VDB), using any relational database
- 2. Select the needed information from the different data sources (tables):
 Filter the data
Filter the data
 Rename table name and attributes
Rename table name and attributes
 Reformat the data (apply any conversion if required)
Reformat the data (apply any conversion if required)
- 3. Transfer the data into the new VDB, by copying the information
- 4. Enhance the VDB
 Set new constraints
Set new constraints
 Merge or fuse data
Merge or fuse data
 Apply additional reformatting, etc.
Apply additional reformatting, etc.
- 5. Update the VDB
 Check anytime availability and completeness at the sources
Check anytime availability and completeness at the sources
 Decide whether to perform an update or a data replacement
Decide whether to perform an update or a data replacement
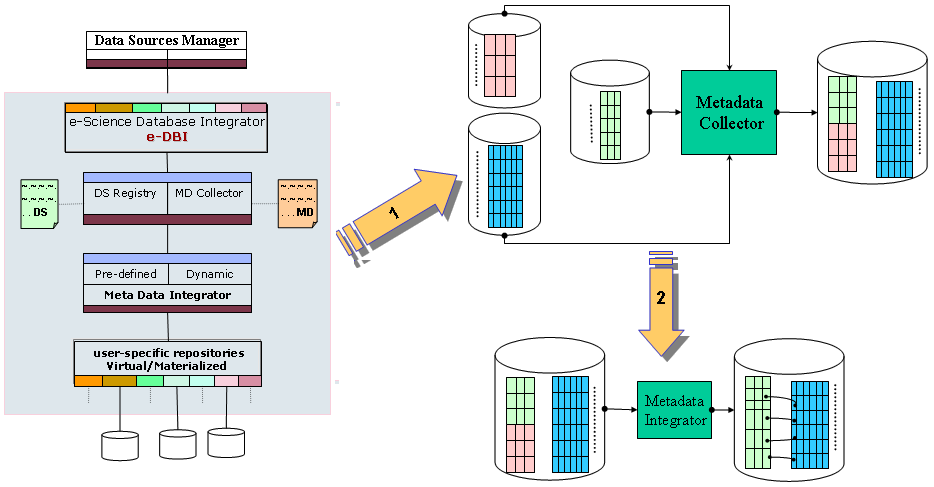
Figure 1. e-DBI: Data Integration Approach
e-DBI Implementation
The e-DBI tool is based on the open source Squirrel SQL project [4]. It supports both (i) the connection to several relational databases, including Oracle, Sybase, and MySQL; and (ii) access to other structured data sources, such as XML content or Excel spreadsheets. The e-DBI was developed to tackle the following challenges:
 Provide an interface that is suitable and convenient for the scientists
Provide an interface that is suitable and convenient for the scientists
 High-level abstraction by hiding unnecessary details
High-level abstraction by hiding unnecessary details
 Enhance the data integration functionalities
Enhance the data integration functionalities
 Hybrid solution between federated and warehousing approaches
Hybrid solution between federated and warehousing approaches
 Facilitate updates for both database schemas and data
Facilitate updates for both database schemas and data
 Oracle, Sybase, MySQL, XML, Excel Spreadsheets, etc.
Oracle, Sybase, MySQL, XML, Excel Spreadsheets, etc.
Downloads
 e-DBI Software (binary 18MB): Download and install e-DBI Software.
e-DBI Software (binary 18MB): Download and install e-DBI Software. e-DBI Client User Manual (e-DBI Manual 967KB).
e-DBI Client User Manual (e-DBI Manual 967KB).
 e-DBI Visual Demos:
e-DBI Visual Demos:
- - e-DBI Register Driver (2mn).
- - e-DBI Register Data Source (2mn).
- - e-DBI Data Integration (5mn).
 e-DBI (Abstract 74KB, Poster 501KB, Presentation 2,343KB)
e-DBI (Abstract 74KB, Poster 501KB, Presentation 2,343KB)
References
 e-DBI: A Framework for Integration of Scientific Data Sources. Data Integration in the Life Sciences Workshop (DILS 2009), July 20-22, 2009. Manchester, UK (Abstract 74KB, Poster 501KB, Presentation 2,343KB).
e-DBI: A Framework for Integration of Scientific Data Sources. Data Integration in the Life Sciences Workshop (DILS 2009), July 20-22, 2009. Manchester, UK (Abstract 74KB, Poster 501KB, Presentation 2,343KB).  H. Afsarmanesh, E.C. Kaletas, A. Benabdelkader, C. Garita, and L. O. Hertzberger. A Reference Architecture for Scientific Virtual Laboratories. In Journal of Future Generation Computer Systems. Vol. 17, N 8, pages 999-1008, June 2001.
H. Afsarmanesh, E.C. Kaletas, A. Benabdelkader, C. Garita, and L. O. Hertzberger. A Reference Architecture for Scientific Virtual Laboratories. In Journal of Future Generation Computer Systems. Vol. 17, N 8, pages 999-1008, June 2001.
 A. R. Jaiswal, C. L. Giles, P. Mitra, and J. Z. Wang. An architecture for creating collaborative semantically capable scientific data sharing infrastructures. In ACM WIDM Workshop, pages 75-82, 2006.
A. R. Jaiswal, C. L. Giles, P. Mitra, and J. Z. Wang. An architecture for creating collaborative semantically capable scientific data sharing infrastructures. In ACM WIDM Workshop, pages 75-82, 2006.
 Squirrel SQL, http://squirrel-sql.sourceforge.net/
Squirrel SQL, http://squirrel-sql.sourceforge.net/
